Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows doctors to directly examine the inside of the uterus and identify any conditions that may be affecting a woman’s fertility. It is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure, meaning it can be used not only to identify uterine problems but also to treat them. At TheFertilife, our team of skilled specialists uses hysteroscopy to diagnose and treat a variety of uterine conditions that could be impacting your reproductive health.
What is Hysteroscopy?
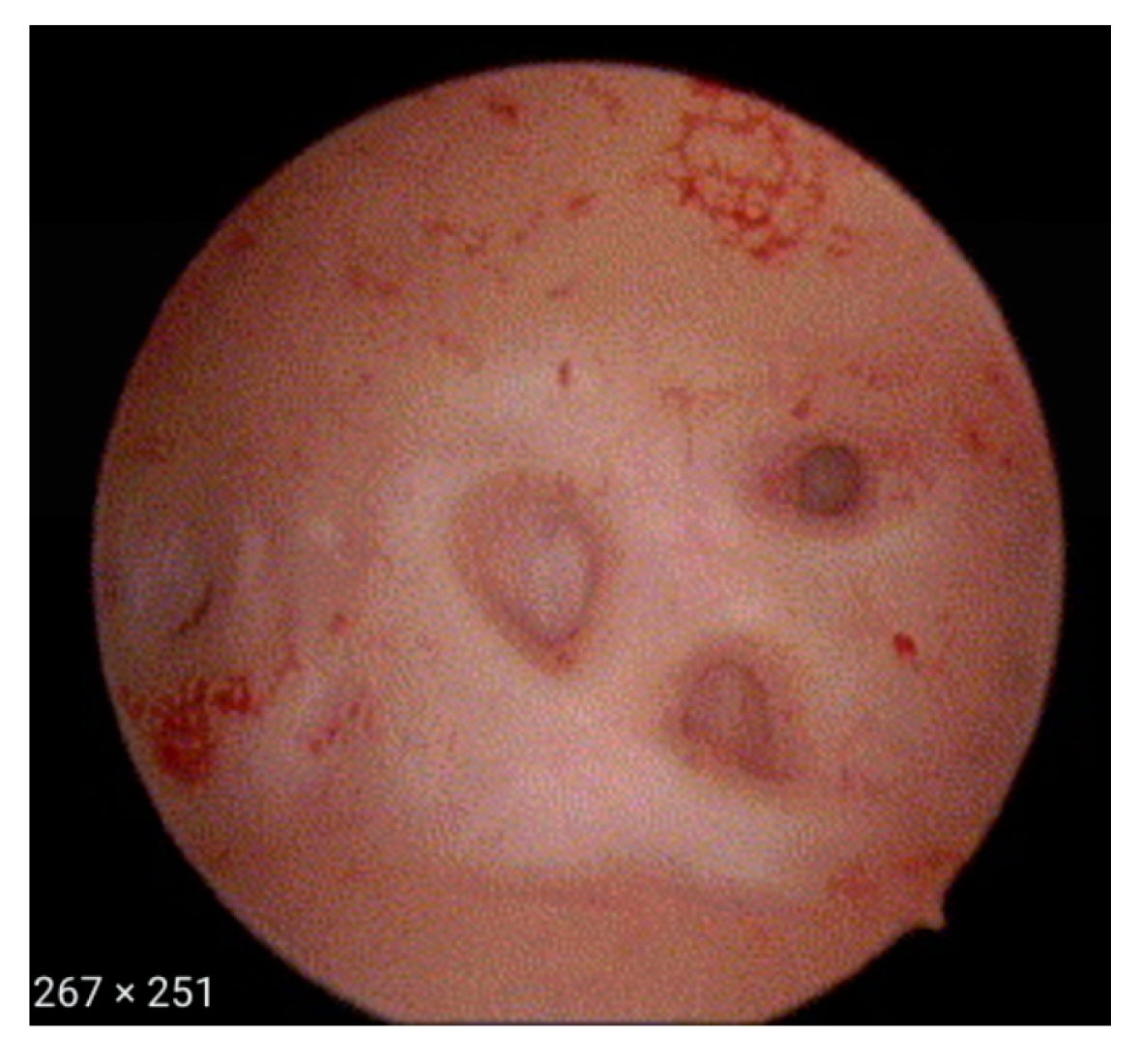
Hysteroscopy involves the insertion of a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope into the uterus through the cervix. The hysteroscope has a camera that sends real-time images to a monitor, allowing the doctor to see the lining of the uterus and any potential issues. It is a safe, minimally invasive procedure that can be done in an outpatient setting or in a hospital, depending on the complexity of the case.
There are two main types of hysteroscopy:
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy: This type is performed to examine the uterine cavity for abnormalities, such as polyps, fibroids, or adhesions. It’s typically done as part of the evaluation of infertility or recurrent miscarriage.
Operative Hysteroscopy: This procedure not only allows the doctor to view the inside of the uterus but also provides the ability to treat any identified issues. For example, polyps, fibroids, or scar tissue (adhesions) can be removed or corrected during the procedure.
When is Hysteroscopy Recommended?
Hysteroscopy is typically recommended for women experiencing infertility, recurrent miscarriage, abnormal bleeding, or other issues related to the uterus. Common reasons for recommending hysteroscopy include:
Infertility: Hysteroscopy can identify structural problems in the uterus, such as fibroids, polyps, or adhesions, which can interfere with conception or implantation.
Recurrent Miscarriages: If a woman has experienced multiple miscarriages, hysteroscopy can help identify anatomical issues in the uterus, such as uterine septum (a congenital abnormality) or adhesions, which may contribute to pregnancy loss.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: If a woman experiences unusual or heavy menstrual bleeding, hysteroscopy can help diagnose conditions like polyps, fibroids, or endometrial cancer.
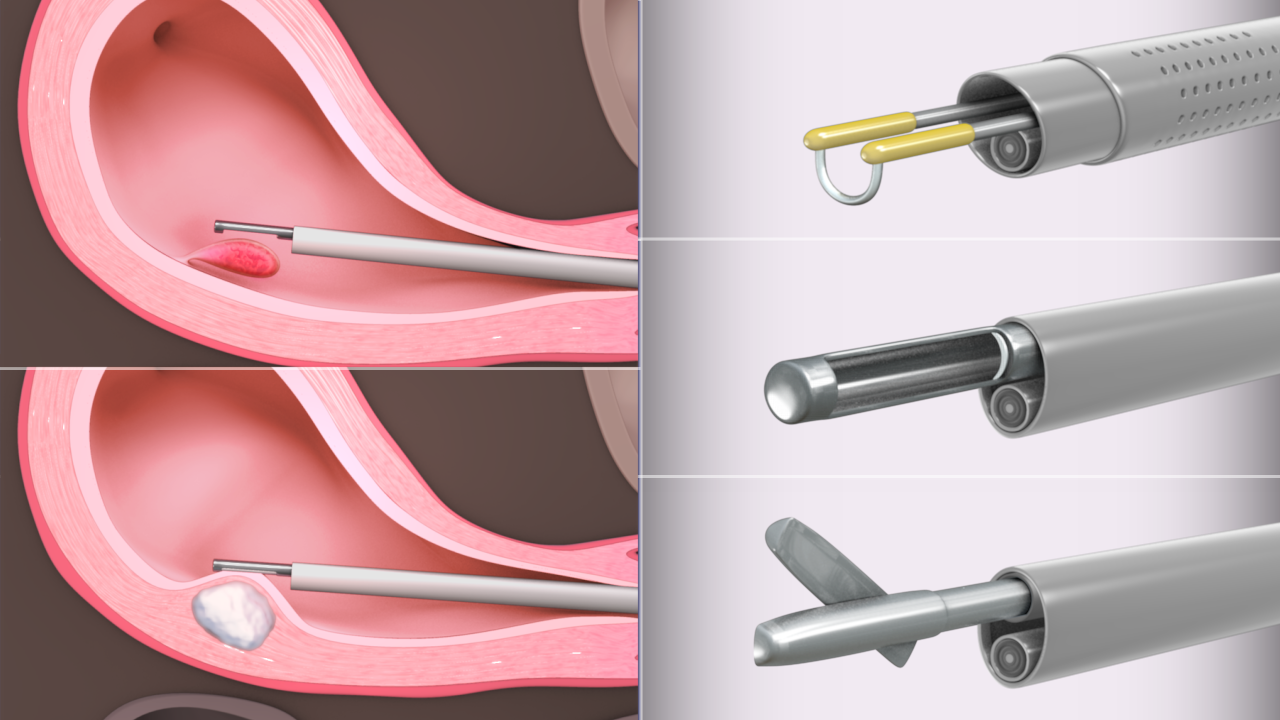
Fibroids: Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can cause pain, heavy bleeding, and infertility. Hysteroscopy can be used to remove submucosal fibroids that are inside the uterine cavity.
Endometrial Polyps: These are growths in the lining of the uterus that can interfere with conception or cause abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is an effective tool to identify and remove polyps.
Asherman’s Syndrome: This condition is characterized by the formation of scar tissue or adhesions in the uterus, often due to previous surgery or infection. Hysteroscopy is commonly used to diagnose and treat this condition by removing the adhesions.
Congenital Uterine Anomalies: In some cases, women may have congenital uterine malformations, such as a septate uterus. Hysteroscopy can be used to correct these structural issues, improving the chances of pregnancy.
How is Hysteroscopy Performed?
Hysteroscopy is typically done on an outpatient basis with local or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient’s comfort level. Here’s a general overview of how the procedure works:
Preparation: The patient may be asked to fast for a few hours before the procedure if general anesthesia is required. A pelvic exam will be performed to check the positioning of the uterus.
Procedure: The hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. The cervix may be dilated slightly if necessary. The uterus is then filled with a sterile fluid (saline or carbon dioxide) to help expand it and allow better visualization.
Examination: The doctor examines the uterine cavity for any abnormalities, such as fibroids, polyps, adhesions, or other structural issues. In a diagnostic hysteroscopy, this may be the extent of the procedure.
Treatment: If any problems are found during the examination, the doctor can use surgical instruments passed through the hysteroscope to treat the issue, such as removing polyps, fibroids, or scar tissue, or correcting uterine malformations.
Completion: Once the procedure is complete, the hysteroscope and any surgical instruments are removed, and the patient is monitored for a short period before being discharged.
Benefits of Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy offers numerous advantages, including:
Minimally Invasive: Hysteroscopy requires only small incisions or no incisions at all (as it’s done through the cervix), which means less pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring.
Accurate Diagnosis: Hysteroscopy provides a direct view of the uterus, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment of uterine conditions than imaging techniques alone, such as ultrasound or X-ray.
Treatment and Diagnosis in One: In an operative hysteroscopy, the physician can not only diagnose problems but also perform treatments during the same procedure, eliminating the need for multiple surgeries.
Short Recovery Time: Recovery from a hysteroscopy is typically quick, and most women can resume normal activities within a few days. Mild cramping, spotting, or discharge may occur for a short period after the procedure.
What to Expect After Hysteroscopy
After the procedure, you may experience some mild cramping, spotting, or vaginal discharge. These symptoms are generally temporary and should subside within a few days. Most women can resume normal activities, including work and light exercise, within 1-2 days, though it’s best to avoid strenuous physical activities for a short time.
If any of the following occur, it is important to contact your healthcare provider:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Heavy bleeding (soaking through a pad every hour)
- Fever or chills
- Foul-smelling discharge
Risks and Considerations
Though hysteroscopy is generally safe, like any medical procedure, it carries some risks. Potential risks include:
- Infection: Though rare, there is a slight risk of infection following the procedure.
- Uterine Perforation: In very rare cases, the hysteroscope may puncture the wall of the uterus.
- Excessive Bleeding: In some cases, there may be more bleeding than expected during or after the procedure.
- Adverse Reactions to Anesthesia: Some patients may experience a reaction to the anesthesia used during the procedure.
However, these complications are rare, and hysteroscopy is considered a safe and effective procedure for diagnosing and treating uterine conditions that affect fertility.
Success Rates of Hysteroscopy in Treating Fertility Issues
Hysteroscopy has been shown to significantly improve fertility outcomes in women with uterine abnormalities. Conditions such as fibroids, polyps, adhesions, or structural anomalies are often treatable through hysteroscopy, and correcting these issues can improve the chances of conception.
- Polyp Removal: Women who have had polyps removed via hysteroscopy may have a higher chance of successful implantation during IVF.
- Fibroid Removal: Women with fibroids that interfere with conception may benefit from the removal of fibroids, improving their fertility chances.
- Adhesion Removal: Women with Asherman’s Syndrome may see improved fertility outcomes after adhesions are removed through hysteroscopy.
Is Hysteroscopy Right for You?
If you are struggling with infertility, recurrent miscarriages, or abnormal bleeding, hysteroscopy may be an excellent option for diagnosing and treating uterine problems. It is a safe, effective procedure that can provide valuable insight into your reproductive health and improve your chances of successful conception.

Best Infertility Doctor in Gurgaon, Dr. Anshika Lekhi, a renowned IVF specialist, offers exceptional infertility treatments.
Pages
Contact Us
- 7505 Basement Bougainville Street, near Supermart 2, Sector 43, Gurugram, Haryana 122009
- 98735 24270
- info@thefertilife.com
Updates
Check New updates below.
Copyright ©2025 | All Rights Reserved.
